
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Drug/Regimen
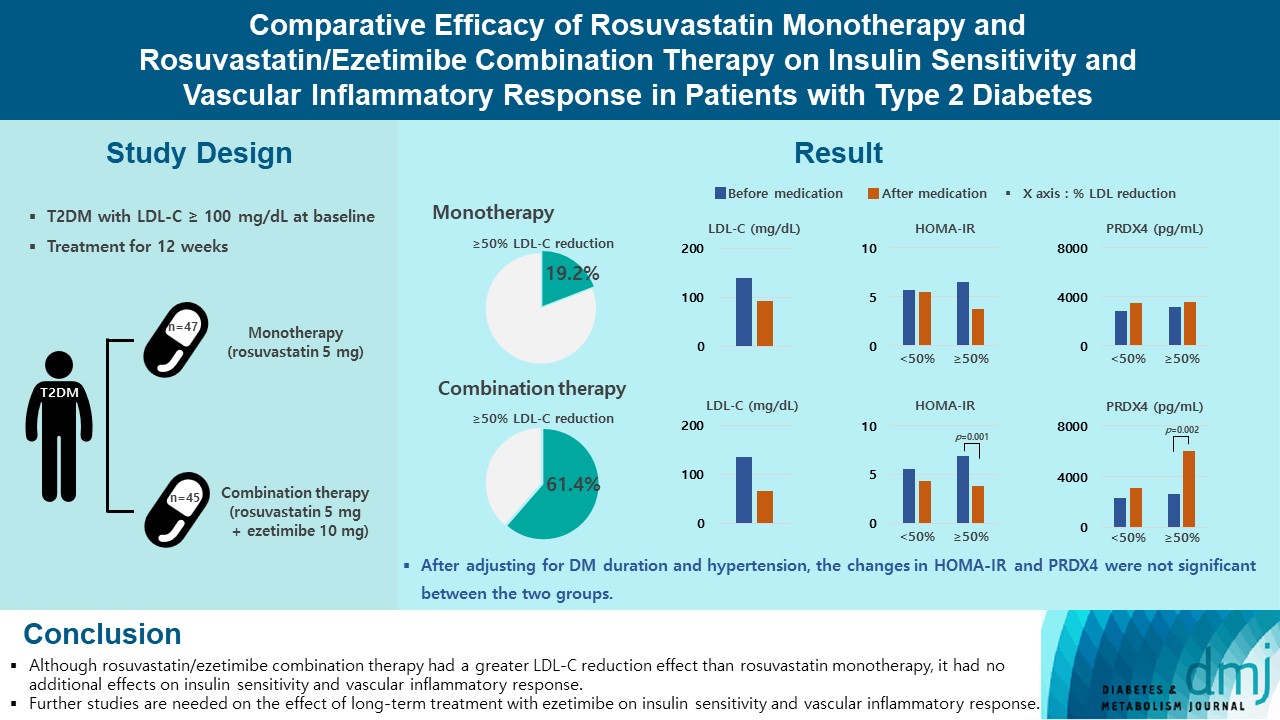
- Comparative Efficacy of Rosuvastatin Monotherapy and Rosuvastatin/Ezetimibe Combination Therapy on Insulin Sensitivity and Vascular Inflammatory Response in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Ji Hye Han, Kyong Hye Joung, Jun Choul Lee, Ok Soon Kim, Sorim Choung, Ji Min Kim, Yea Eun Kang, Hyon-Seung Yi, Ju Hee Lee, Bon Jeong Ku, Hyun Jin Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(1):112-121. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0402
- 1,997 View
- 221 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) induces endothelial dysfunction and inflammation, which are the main factors for atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. The present study aimed to compare the effects of rosuvastatin monotherapy and rosuvastatin/ezetimibe combination therapy on lipid profile, insulin sensitivity, and vascular inflammatory response in patients with T2DM.
Methods
A total of 101 patients with T2DM and dyslipidemia were randomized to either rosuvastatin monotherapy (5 mg/day, n=47) or rosuvastatin/ezetimibe combination therapy (5 mg/10 mg/day, n=45) and treated for 12 weeks. Serum lipids, glucose, insulin, soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1), and peroxiredoxin 4 (PRDX4) levels were determined before and after 12 weeks of treatment.
Results
The reduction in low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) by more than 50% from baseline after treatment was more in the combination therapy group. The serum sICAM-1 levels increased significantly in both groups, but there was no difference between the two groups. The significant changes in homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) and PRDX4 were confirmed only in the subgroup in which LDL-C was reduced by 50% or more in the combination therapy group. However, after adjusting for diabetes mellitus duration and hypertension, the changes in HOMA-IR and PRDX4 were not significant between the two groups.
Conclusion
Although rosuvastatin/ezetimibe combination therapy had a greater LDL-C reduction effect than rosuvastatin monotherapy, it had no additional effects on insulin sensitivity and vascular inflammatory response. Further studies are needed on the effect of long-term treatment with ezetimibe on insulin sensitivity and vascular inflammatory response. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Combining Ezetimibe and Rosuvastatin: Impacts on Insulin Sensitivity and Vascular Inflammation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Eun Roh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(1): 55. CrossRef
- Combining Ezetimibe and Rosuvastatin: Impacts on Insulin Sensitivity and Vascular Inflammation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Others
- Serum R-Spondin 1 Is a New Surrogate Marker for Obesity and Insulin Resistance
- Yea Eun Kang, Ji Min Kim, Hyon-Seung Yi, Kyong Hye Joung, Ju Hee Lee, Hyun Jin Kim, Bon Jeong Ku
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(3):368-376. Published online October 23, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0066
- 5,001 View
- 75 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Recent
in vivo studies indicated that R-spondin 1 (RSPO1) regulates food intake and increases insulin secretion, but its role in humans remains unknown. This study investigated the association between serum levels of RSPO1 and diverse metabolic parameters in humans.Methods The study population consisted of 43 subjects with newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus, and 79 non-diabetic participants. Serum levels of RSPO1 were measured using the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The relationships between circulating RSPO1 and diverse metabolic parameters were analyzed.
Results Circulating RSPO1 levels increased to a greater extent in the obese group than in the lean group. Moreover, serum levels of RSPO1 were higher in the insulin-resistant group than in the insulin-sensitive group. Serum levels of RSPO1 were significantly correlated with a range of metabolic parameters including body mass index, fasting C-peptide, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance index, and lipid profile. Moreover, levels were significantly associated with insulin resistance and obesity in non-diabetic subjects.
Conclusion This study demonstrated the association between serum levels of RSPO1 and a range of metabolic parameters in humans. Serum levels of RSPO1 are significantly related to obesity and insulin resistance, although the precise mechanisms remain unknown.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- LGR4: A New Receptor Member in Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases
Ningning Zhang, Mingyang Yuan, Jiqiu Wang
Endocrine Reviews.2023; 44(4): 647. CrossRef - R-Spondin1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in infertile women with polycystic ovary syndrome: relationships with insulin resistance and other parameters
Tuğba GÜRBÜZ, Oya GÖKMEN, Asena AYAR MADENLİ, Berna DİLBAZ
Journal of Health Sciences and Medicine.2023; 6(2): 449. CrossRef - An early prediction model for type 2 diabetes mellitus based on genetic variants and nongenetic risk factors in a Han Chinese cohort
Jinjin Li, Qun Ye, Hongxiao Jiao, Wanyao Wang, Kai Zhang, Chen Chen, Yuan Zhang, Shuzhi Feng, Ximo Wang, Yubao Chen, Huailin Gao, Fengjiang Wei, Wei-Dong Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Emerging Therapeutic Strategies for Attenuating Tubular EMT and Kidney Fibrosis by Targeting Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling
Lichao Hu, Mengyuan Ding, Weichun He
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Does Serum R-Spondin-1 Play a Role in PCOS Pathophysiology?
Osman BAŞPINAR, Yasin ŞİMŞEK, Derya KOÇER, Oğuzhan Sıtkı DİZDAR, Hatice KAYIŞ TOPALOĞLU
Genel Tıp Dergisi.2022; 32(5): 490. CrossRef - Silencing of RSPO1 mitigates obesity-related renal fibrosis in mice by deactivating Wnt/β-catenin pathway
Xuesong Su, Guangyu Zhou, Mi Tian, Si Wu, Yanqiu Wang
Experimental Cell Research.2021; 405(2): 112713. CrossRef - Exosome miR‐27a‐3p secreted from adipocytes targets ICOS to promote antitumor immunity in lung adenocarcinoma
Xuehan Fan, Jingya Wang, Tingting Qin, Yujia Zhang, Wenting Liu, Kaiting Jiang, Dingzhi Huang
Thoracic Cancer.2020; 11(6): 1453. CrossRef - Integrative Analyses of Genes Associated with Subcutaneous Insulin Resistance
Manoj Kumar Pujar, Basavaraj Vastrad, Chanabasayya Vastrad
Biomolecules.2019; 9(2): 37. CrossRef
- LGR4: A New Receptor Member in Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases
- Others
- Serum Soluble Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Level Increase in Patients Newly Diagnosed with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Ji Min Kim, Sorim Choung, Kyong Hye Joung, Ju Hee Lee, Hyun Jin Kim, Bon Jeong Ku
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(4):343-347. Published online May 2, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.0082
- 4,312 View
- 50 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader We analyzed circulating soluble epidermal growth factor receptor (sEGFR) levels in humans. Serum sEGFR levels were higher in subjects with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus compared with controls. Serum sEGFR was positively correlated with glycosylated hemoglobin and serum glucose and negatively correlated with serum insulin and C-peptide levels.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Increased serum extrachromosomal circular DNA SORBS1circle level is associated with insulin resistance in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus
Xiang Kong, Shu-jun Wan, Tian-bing Chen, Lan Jiang, Yu-jie Xing, Ya-ping Bai, Qiang Hua, Xin-ming Yao, Yong-li Zhao, Hong-mei Zhang, De-guo Wang, Qing Su, Kun Lv
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Pilot Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies Novel Markers of Metabolic Syndrome in Patients with Psoriasis
Seung-Min Oh, Su-Kang Kim, Hye-Jin Ahn, Ki-Heon Jeong
Annals of Dermatology.2023; 35(4): 285. CrossRef - Effect of cholesterol-lowering agents on soluble epidermal growth factor receptor level in type 2 diabetes and hypercholesterolemia
Jun Choul Lee, Kyong Hye Joung, Ji Min Kim, Seon Mee Kang, Hyun Jin Kim, Bon Jeong Ku
Medicine.2022; 101(34): e30287. CrossRef - Soluble EGFR, a hepatokine, and adipsin, an adipokine, are biomarkers correlated with distinct aspects of insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes subjects
Mayu Kyohara, Jun Shirakawa, Tomoko Okuyama, Yu Togashi, Ryota Inoue, Jinghe Li, Daisuke Miyashita, Yasuo Terauchi
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidermal growth factor protects against myocardial ischaemia reperfusion injury through activating Nrf2 signalling pathway
Jun Ma, Ge Jin
Free Radical Research.2019; 53(3): 313. CrossRef
- Increased serum extrachromosomal circular DNA SORBS1circle level is associated with insulin resistance in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Others
- Clinical Implications of Using Post-Challenge Plasma Glucose Levels for Early Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Older Individuals
- Kyong Hye Joung, Sang Hyun Ju, Ji Min Kim, Sorim Choung, Jae Min Lee, Kang Seo Park, Hyun Jin Kim, Bon Jeong Ku
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(2):147-154. Published online February 13, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.42.2.147
- 4,631 View
- 36 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The aim of this study was to explore the differences in the clinical characteristics and diagnostic rates of diabetes mellitus (DM) according to various criteria in different age groups and to evaluate the efficacy of each criterion for screening older patients.
Methods We studied 515 patients and measured the fasting plasma glucose level (FPG), 2-hour plasma glucose level after the 75 g oral glucose tolerance test (2-hour postload glucose [2-h PG]), and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) for re-evaluation of hyperglycemia without a history of diabetes. Patients with newly diagnosed DM were grouped by age as younger (<65 years) or older (≥65 years).
Results Older patients had significantly lower HbA1c, FPG, and 2-h PG levels and a higher homeostatic level of pancreatic β-cell function compared with younger patients (
P <0.001). The older group had the lowest diagnostic rate when using the FPG level (45.5%) and the highest diagnostic rate when using the 2-h PG level (84.6%). These results were mostly due to the higher frequency of isolated post-challenge hyperglycemia in the older patients than in the younger group (28.8% vs. 9.2%). The use of both the FPG and HbA1c levels significantly enhanced the low diagnostic power when employing only the FPG levels in the older group (71.2% vs. 45.5%).Conclusion In the older patients, the 2-h PG level was the most accurate diagnostic criterion. When we consider the costs and convenience, a combination of the FPG and HbA1c criteria may be recommended as a screening test for DM in older people.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- International Diabetes Federation Position Statement on the 1-hour post-load plasma glucose for the diagnosis of intermediate hyperglycaemia and type 2 diabetes
Michael Bergman, Melania Manco, Ilhan Satman, Juliana Chan, Maria Inês Schmidt, Giorgio Sesti, Teresa Vanessa Fiorentino, Muhammad Abdul-Ghani, Ram Jagannathan, Pramod Kumar Thyparambil Aravindakshan, Rafael Gabriel, Viswanathan Mohan, Martin Buysschaert,
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 209: 111589. CrossRef - A unified technique for entropy enhancement based diabetic retinopathy detection using hybrid neural network
Fatima, Muhammad Imran, Anayat Ullah, Muhammad Arif, Rida Noor
Computers in Biology and Medicine.2022; 145: 105424. CrossRef - In-silico identification of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)α/γ agonists from Ligand Expo Components database
Xiao-Yan Feng, Ting-Ting Ding, Ya-Ya Liu, Wei-Ren Xu, Xian-Chao Cheng
Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics.2021; 39(5): 1853. CrossRef
- International Diabetes Federation Position Statement on the 1-hour post-load plasma glucose for the diagnosis of intermediate hyperglycaemia and type 2 diabetes
- Others
- Effect of Atorvastatin on Growth Differentiation Factor-15 in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Dyslipidemia
- Ji Min Kim, Min Kyung Back, Hyon-Seung Yi, Kyong Hye Joung, Hyun Jin Kim, Bon Jeong Ku
- Diabetes Metab J. 2016;40(1):70-78. Published online February 19, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.1.70
- 4,163 View
- 33 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Elevated serum levels of growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15) are associated with type 2 diabetes. Therefore, the effects of atorvastatin on metabolic parameters and GDF-15 levels in patients with type 2 diabetes and dyslipidemia were evaluated.
Methods In this prospective randomized trial from February 2013 to March 2014, 50 consecutive type 2 diabetic patients with a low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels ≥100 mg/dL were enrolled. The patients were divided into two groups based on the amount of atorvastatin prescribed, 10 mg/day (
n =23) or 40 mg/day (n =27). The effect of atorvastatin on metabolic parameters, including lipid profiles and GDF-15 levels, at baseline and after 8 weeks of treatment were compared.Results The baseline metabolic parameters and GDF-15 levels were not significantly different between the two groups. After 8 weeks of treatment, the total cholesterol (TC) and LDL-C levels were significantly decreased in both groups. The mean changes in TC and LDL-C levels were more significant in the 40 mg atorvastatin group. The GDF-15 level was decreased in the 10 mg atorvastatin group, from 1,460.6±874.8 to 1,451.0±770.8 pg/mL, and was increased in the 40 mg atorvastatin group, from 1,271.6±801.0 to 1,341.4±855.2 pg/mL. However, the change in the GDF-15 level was not statistically significant in the 10 or 40 mg atorvastatin group (
P =0.665 andP =0.745, respectively).Conclusion The GDF-15 levels were not significantly changed after an 8-week treatment with atorvastatin in type 2 diabetic patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The relationship of Growth differentiation factor-15 with renal damage and dyslipidemia in non-albuminuric and albuminuric Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus
Hasan Esat Yücel, Bilal İlanbey
Medical Science and Discovery.2022; 9(6): 334. CrossRef - Comparative effectiveness of statins on non-high density lipoprotein cholesterol in people with diabetes and at risk of cardiovascular disease: systematic review and network meta-analysis
Alexander Hodkinson, Dialechti Tsimpida, Evangelos Kontopantelis, Martin K Rutter, Mamas A Mamas, Maria Panagioti
BMJ.2022; : e067731. CrossRef - The Cytokine Growth Differentiation Factor-15 and Skeletal Muscle Health: Portrait of an Emerging Widely Applicable Disease Biomarker
Boel De Paepe
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(21): 13180. CrossRef - Biomarkers of subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with psoriasis
Hannah Kaiser, Xing Wang, Amanda Kvist-Hansen, Martin Krakauer, Peter Michael Gørtz, Benjamin D. McCauley, Lone Skov, Christine Becker, Peter Riis Hansen
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Growth differentiation factor-15 regulates oxLDL-induced lipid homeostasis and autophagy in human macrophages
Kathrin Ackermann, Gabriel A. Bonaterra, Ralf Kinscherf, Anja Schwarz
Atherosclerosis.2019; 281: 128. CrossRef
- The relationship of Growth differentiation factor-15 with renal damage and dyslipidemia in non-albuminuric and albuminuric Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Cardio-Metabolic Features of Type 2 Diabetes Subjects Discordant in the Diagnosis of Metabolic Syndrome
- Sa Rah Lee, Ying Han, Ja Won Kim, Ja Young Park, Ji Min Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Mi-Kyoung Park, Hye-Jeong Lee, Duk Kyu Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2012;36(5):357-363. Published online October 18, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2012.36.5.357
- 3,430 View
- 28 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The aim of this study is to investigate the cardio-metabolic parameters and surrogate markers of insulin resistance in a discordant group of type 2 diabetes (T2DM) subjects who satisfy the Adults Treatment Panel (ATP) III criteria, but not the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) criteria, for metabolic syndrome (MetS).
Methods We assessed the prevalence of MetS in T2DM subjects (
n =167) who were selected from subjects registered at the diabetes center of Dong-A University Medical Center. We used the ATP III criteria and the IDF criteria for the diagnosis of MetS and sorted the subjects into 2 MetS groups: one group diagnosed per ATP III criteria (MetSa ) and one diagnosed per IDF criteria (MetSi ). We then compared the clinical characteristics, metabolic parameters (homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance, aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, and uric acid values) and co-morbidities (prevalence of microalbuminuria, fatty liver, and cardiovascular disease) between the MetSa , MetSi , and discordant MetS groups.Results The prevalence of MetS in the MetS
a group (73.6%) was higher than in the MetSi group (62.2%). The MetS prevalence in the discordant group was 11.4%. The discordant group showed no significant differences in clinical characteristics (except waist circumference and body mass index), metabolic parameters, or prevalence of co-morbidities, as compared with subjects with MetS by both criteria.Conclusion In this study, cardio-metabolic features of the subjects diagnosed with MetS using ATP III criteria, but not IDF criteria, are not significantly different from those of subjects diagnosed with MetS using both criteria.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical analysis of the relationship between cystatin C and metabolic syndrome in the elderly
Ping Liu, Shujian Sui, Dongling Xu, Xiaowei Xing, Caixia Liu
Revista Portuguesa de Cardiologia.2014; 33(7-8): 411. CrossRef - Resolvin D1 reduces ER stress-induced apoptosis and triglyceride accumulation through JNK pathway in HepG2 cells
Tae Woo Jung, Hwan-Jin Hwang, Ho Cheol Hong, Hae Yoon Choi, Hye Jin Yoo, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2014; 391(1-2): 30. CrossRef - Clinical analysis of the relationship between cystatin C and metabolic syndrome in the elderly
Ping Liu, Shujian Sui, Dongling Xu, Xiaowei Xing, Caixia Liu
Revista Portuguesa de Cardiologia (English Edition).2014; 33(7-8): 411. CrossRef
- Clinical analysis of the relationship between cystatin C and metabolic syndrome in the elderly
- Adiponectin Concentrations in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with or without Metabolic Syndrome.
- Ja Young Park, Ja Won Kim, Ji Min Kim, Ying Han, Soo Kyung Park, Ji Young Mok, Mi Kyoung Park, Hye Jeong Lee, Duk Kyu Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2008;32(3):224-235. Published online June 1, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2008.32.3.224
- 2,379 View
- 20 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Adipocytes produce several adipokines that modulate insulin action as well as glucose and lipid metabolism. The aim of this study was to evaluate the relationship between serum adiponectin concentrations and metabolic syndrome (MS) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. METHODS: This study included 127 type 2 diabetic patients (males 63, females 64). The subjects were divided into two groups as with or without metabolic syndrome (MS(+) or MS(-)). The MS was diagnosed by International Diabetes Federation. Serum adiponectin, leptin, fasting plasma insulin, glucose, glycated hemoglobin, lipid profile, white blood corpuscle (WBC), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), uric acid and C-reactive protein (CRP) were examined. RESULTS: Serum adiponectin concentrations were significantly lower in MS(+) than MS(-) (4.8 +/- 2.4 microgram/mL vs 7.6 +/- 5.8 microgram/mL, 7.6 +/- 3.7 microgram/mL vs 11.5 +/- 7.2 microgram/mL, P < 0.05 in males and females). After adjustment for age and body mass index (BMI), in MS (+), the serum levels of adiponectin correlated positively with high density lipoprotein - cholesterol (HDL-C) and negatively with height, body weight, ALT and CRP. In MS(-), the serum levels of adiponectin correlated positively with HDL-C and negatively with diastolic blood pressure (DBP), triglyceride and CRP. By multiple regression analysis, no parameters were independently correlated with serum adiponectin concentrations in MS(+), while DBP and HDL-C were independently related to serum adiponectin concentrations in MS(-). CONCLUSION: Serum adiponectin concentrations were lower in type 2 diabetic patients with MS than without MS. There were no significant parameters related to decrease serum adiponectin concentrations in MS. But further study is needed to confirm this result. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Urinary adiponectin concentration is positively associated with micro- and macro-vascular complications
Won Seon Jeon, Ji Woo Park, Namseok Lee, Se Eun Park, Eun Jung Rhee, Won Young Lee, Ki Won Oh, Sung Woo Park, Cheol-Young Park, Byung-Soo Youn
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2013;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Plasma Osteoprotegerin with Adiponectin and Difference according to Obesity in Men with Metabolic Syndrome
Woori Na, Cheongmin Sohn
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2011; 16(6): 762. CrossRef - The Effects of 12-Weeks Intensive Intervention Program on Cardiovascular Risk Factors, Adipocytokines and Nutrients Intakes in Industrial Male Workers
Kieun Moon, Ill Keun Park, Yeon Sang Jo, Yun Kyun Chang, Yun Mi Paek, Tae In Choi
The Korean Journal of Nutrition.2011; 44(4): 292. CrossRef - Relationship between Nutrients Intakes, Dietary Quality, and Serum Concentrations of Inflammatory Markers in Metabolic Syndrome Patients
Misung Kim, Juyoung Kim, Wookyung Bae, Sohye Kim, Yesong Lee, Woori Na, Cheongmin Sohn
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2011; 16(1): 51. CrossRef - Prevalence of Pancreatic Cancer in Diabetics and Clinical Characteristics of Diabetes-associated with Pancreatic Cancer - Comparison between Diabetes with and without Pancreatic Cancer -
Seung Goun Hong, Jae Seon Kim, Sung Joo Jung, Moon Kyung Joo, Beom Jae Lee, Jong Eun Yeon, Jong-Jae Park, Kwan Soo Byun, Young-Tae Bak
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2009; 54(3): 167. CrossRef
- Urinary adiponectin concentration is positively associated with micro- and macro-vascular complications
- Prevention of Diabetes by Fenofibrate in OLETF Rats: Hepatic Mechanism for Reducing Visceral Adiposity.
- Hye Jeong Lee, Mi Kyoung Park, Kyung Il Lee, Young Jun An, Ji Min Kim, Ja Young Park, Young Han, Sook Hee Hong, Sun Seob Choi, Young Hyun Yoo, Joon Duk Suh, Duk Kyu Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2007;31(1):63-74. Published online January 1, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2007.31.1.63
- 2,129 View
- 18 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The aim of this study is to evaluate the hepatic mechanism of fenofibrate that has the diabetes protective action in rats. METHODS: We chose OLETF rats and divided them into three groups. Fenofibrate (DF) group was fed with diet and fenofibrate (300 mg/kg/day). Paired feeding (Dd) group and free diet (DD) group were fed with diet. After 36 weeks of treatment, all the rats were sacrificed. RESULTS: The fasting blood glucose level of DF group (8.5 +/- 0.9 mmol/L) showed normal. The fasting blood glucose level of Dd group (22.4 +/- 3.0 mmol/L) and DD group (16.9 +/- 3.7 mmol/L) showed significantly increased than that of DF group (P < 0.01, respectively). The body weight, visceral adipose tissue and subcutaneous adipose tissue of DF group were significantly decreased compared to those of Dd and DD groups (P < 0.01, P < 0.05, P < 0.05). DF group showed significantly increased state-3 respiration rate, ATP synthetic activity, state-4 respiration rate and their blood beta-keton body levels than those of control groups (P < 0.01, respectively). DF group showed normal morphology of hepatocytes but DD and Dd groups showed hepatic steatosis with mitochondrial swellings. CONCLUSION: Chronic fenofibrate treatment prevents the development of diabetes in OLETF rats with inhibiting gain of body weight and abdominal adiposity. The hepatic mechanism for reducing visceral adiposity is that fenofibrate leads to increasing oxidative phosphorylation, uncoupling and ketogenesis as well as increasing beta-oxidation of fatty acids. Moreover, fenofibrate treatment prevents the development of hepatic steatosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Differences of Metabolic Syndrome Risk Factors according to Obesity and Abdominal Obesity in Elderly Korean Women
Kyung-A Shin
The Korean Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science.2016; 48(4): 304. CrossRef - Effects of Soybean and DJI Chungkukjang Powder on Blood Glucose and Serum Lipid Reduction in db/db Mice
Jae-Joon Lee, Ah-Ra Kim, Hae-Choon Chang, Hae-Ok Jung, Myung-Yul Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2012; 41(8): 1086. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of fat and muscle proteins in fenofibratefed type II diabetic OLETF rats: the fenofibrate-dependent expression of PEBP or C11orf59 protein
Jong-Ryeal Hahm, Jin-Sook Ahn, Hae-Sook Noh, Seon-Mi Baek, Ji-Hye Ha, Tae-Sik Jung, Yong-Jun An, Duk-Kyu Kim, Deok-Ryong Kim
BMB Reports .2010; 43(5): 337. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of fat and muscle proteins in fenofibratefed type II diabetic OLETF rats: the fenofibrate-dependent expression of PEBP or C11orf59 protein
Jong-Ryeal Hahm, Jin-Sook Ahn, Hae-Sook Noh, Seon-Mi Baek, Ji-Hye Ha, Tae-Sik Jung, Yong-Jun An, Duk-Kyu Kim, Deok-Ryong Kim
BMB Reports.2010; 43(5): 337. CrossRef
- The Differences of Metabolic Syndrome Risk Factors according to Obesity and Abdominal Obesity in Elderly Korean Women
- Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Type 2 DM Patients with Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver.
- Ji Min Kim, Ja Young Park, Hyn Kyung Nam, Ja Won Kim, Su Kyung Park, Kyung Jin Nam, Mi Kyoung Park, Hye Jeong Lee, Duk Kyu Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2006;30(6):442-449. Published online November 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2006.30.6.442
- 2,008 View
- 16 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Non-alcoholic fatty liver is rendered as one component of metabolic syndrome (MS). We evaluated the prevalence of MS as well as clinical and laboratory characteristics of Type 2 DM patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver. METHODS: Fatty liver group (n = 71) who showed significant fatty change by ultrasonography and age, sex matched control group (n = 40) were studied retrospectively. We compared demographic and laboratory findings and prevalence of MS by modified WHO criteria and new IDF criteria between both groups. RESULTS: There were no significant difference in age, DM duration, BMI, prevalence of hypertension, coronary artery disease, CVA, diabetic retinopathy, neuropathy, nephropathy between both groups. In fatty liver group, the plasma level of FBS, TG, ALT, total protein, albumin and GGT were significantly higher than those of control group (P = 0.033, P = 0.000, P = 0.002, P = 0.008, P = 0.003, P = 0.001). The plasma levels of HDL-C in fatty liver group were significantly lower than those of control group (P = 0.013). The plasma level of FBS, FFA, TG, total protein, albumin, ALT, HOMA(IR) and BMI were significantly related to the severity of fatty liver. The prevalence of MS in fatty liver group was significantly higher than that of control group by modified WHO criteria (P = 0.001) or new IDF criteria (P = 0.036). CONCLUSION: Type 2 DM patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver frequently accompanied the metabolic syndrome. They showed nonspecific changes in the liver function tests. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cardio-Metabolic Features of Type 2 Diabetes Subjects Discordant in the Diagnosis of Metabolic Syndrome
Sa Rah Lee, Ying Han, Ja Won Kim, Ja Young Park, Ji Min Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Mi-Kyoung Park, Hye-Jeong Lee, Duk Kyu Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2012; 36(5): 357. CrossRef - Metabolic Syndrome and Serum Alanine Aminotransferase Levels in Korean Adults : The Third Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES III), 2005.
Mi Ah Han, So Yeon Ryu, Jong Park, Myung Geun Kang, Ki Soon Kim
Korean Journal of Epidemiology.2008; 30(1): 25. CrossRef
- Cardio-Metabolic Features of Type 2 Diabetes Subjects Discordant in the Diagnosis of Metabolic Syndrome

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





